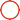
Perfect Cutting Edge Carbide Threading Inserts For Metric Thread Precision Tooth Shape
Product Details:
Get Best Price Contact Now|
Detail Information |
|||
| Name: | Carbide Cutting Inserts | Material: | Tungsten Carbide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application: | Thread Turning Tool | Workpiece: | Steel\ Stainless\ Cast Iron |
| Advantage: | Good Perfermance,wear Resistance | Size: | Custom |
| High Light: | carbide insert cutting tools,carbide cutting inserts |
||
Product Description
Perfect Cutting Edge Carbide Threading Inserts For Metric Thread Precision Tooth Shape
Detailed Product Description
|
Application: |
Thread Turning |
Material: |
Cemented Carbide |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Coating: |
PVD |
Standard: |
ISO |
|
Grade: |
MP2215 |
Type: |
Various |
Carbide Threading Inserts for ISO Metric Thread with Precision Tooth Shape and Perfect Cutting Edge
Feature Advantage:
-
The ISO standard thread series is available in various types.
-
Observed under a microscope of 40 times, the perfect edge grinding and passivation accuracy.
-
The workpiece angle error is controlled at ±0.5 degrees.
-
High-quality cemented carbide substrate, high toughness, high wear resistance and versatility.
-
High-precision tooth shape for high-quality, high-precision thread machining of steel, stainless steel, and difficult-to-cut materials.
-
Insert life and turning thread quality are completely comparable to European and American first-line brands.
Type:
|
Serial |
Size |
Pitch |
MP2215 |
||
|
ISO: ISO 965-1980 DIN 13 |
16 |
Right/Left |
External |
0.5-3.0 mm |
★ |
|
ISO: ISO 965-1980 DIN 13 |
16 |
Right/Left |
Internal |
0.5-3.0 mm |
★ |
|
ISO: ISO 965-1980 DIN 13 |
22 |
Right/Left |
External |
3.5-6.0 mm |
★ |
|
ISO: ISO 965-1980 DIN 13 |
22 |
Right/Left |
Internal |
3.5-6.0 mm |
★ |
|
Wyeth: ISO 228/1:1982 DIN 259,B.S.84: 1956 |
16 |
Right/Left |
External |
8-19 t/inch |
★ |
|
Wyeth: ISO 228/1:1982 DIN 259,B.S.84: 1956 |
16 |
Right/Left |
Internal |
8-19 t/inch |
★ |
|
UN: ASME B1.1 - 1989 |
16 |
Right/Left |
External |
8-24 t/inch |
★ |
|
UN: ASME B1.1 - 1989 |
16 |
Right/Left |
Internal |
8-24 t/inch |
★ |
|
Standard SSPT: ISO 7/1:1994 B.S.21:1985 |
16 |
Right/Left |
External |
11-28 t/inch |
★ |
|
Standard SSPT: ISO 7/1:1994 B.S.21:1985 |
16 |
Right/Left |
Internal |
11-28 t/inch |
★ |
|
Standard NPT: ASME B1.20.1-1983 |
16 |
Right/Left |
External |
8-27 t/inch |
★ |
|
Standard NPT: ASME B1.20.1-1983 |
16 |
Right/Left |
Internal |
8-27 t/inch |
★ |
Technical Information:
-
ISO standard thread for industrial machinery industry.
-
Turning threads are common operations on CNC machines. The use of indexable tools to cut threads enables safe and high productivity of the process.
-
The feed of the machine is the most important factor in turning the thread: it must be equal to the pitch, which is the distance between a point on the thread and the corresponding point of the adjacent thread. The fit between the pitch and the feed per revolution is accomplished by controlling subroutines in the CNC machine.
-
Thread turning should initially consider three aspects to determine the best method and tool selection for threading:
-
Main parameters of the thread:
-
External or internal thread
-
Thread type
-
Pitch
-
Right or left hand thread
-
Tolerance
-
-
Workpiece material properties, shape and quantity
-
Whether the workpiece is safely clamped
-
Whether there is any problem with chip removal
-
Workpiece batch
-
-
Machine parameter
-
Stability, power and torque requirements, especially for larger diameter threading
-
Workpiece clamping condition
-
Threading cycle should be easy to program
-
Cutting fluid and coolant
-
-
Recommended Cutting Parameters:
-
The following cutting parameters are the recommended range values, and the actual values can be appropriately taken as high values.
-
When testing new cutting speeds, you should carefully check the condition of the cutting edge.
-
For stainless steel thread cutting, a high enough cutting speed should be used to avoid the formation of built-up edge.
-
When cutting small pitch threads and using small nose radius tools, the cutting parameters should be appropriately reduced.
|
ISO |
Material |
Unit Cutting Force N/mm 2 |
Hardness HB |
Speed m/min |
|
|
P |
Carbon Steel |
C=0.15% C=0.35% C=0.60% |
1900 2100 2250 |
125 150 200 |
150-175 140-155 130-145 |
|
P |
Alloy Steel |
Annealing Hardened Hardened Hardening |
2100 2600 2700 2850 |
180 275 300 350 |
110-130 80-100 70-90 60-80 |
|
P |
High Alloy Steel |
Annealing Hardening |
2600 3900 |
200 325 |
90-115 70-90 |
|
P |
Cast Steel |
Non-alloy Low alloy High alloy Martensite Steel 12% Mn |
2000 2500 2700 3600 |
180 200 225 250 |
180-210 90-115 90-115 40-50 |
|
M |
Stainless Steel |
Austenite |
2450 |
180 |
110-130 |
|
M |
Stainless Steel |
Martensite / Ferrite |
2300 |
200 |
130-170 |
|
K |
Malleable Cast Iron |
Ferrite Pearlite |
1100 1100 |
130 230 |
110-140 85-105 |
|
K |
Gray Cast Iron |
Low Tensile Strength High Tensile Strength |
1100 1500 |
180 260 |
110-140 90-115 |
|
K |
Ductile Iron |
Ferrite Pearlite |
1100 1800 |
160 250 |
110-130 80-100 |
|
N |
Aluminum Alloy |
Not Aged Aging Treatment |
500 800 |
60 100 |
1300-1450 450-500 |
|
N |
Cast Aluminum Alloy |
Not Aged Aging Treatment |
750 900 |
75 90 |
430-470 250-290 |
|
S |
Heat Resistant Alloy |
Nickel Base |
3000 3050 |
200 280 |
35-50 25-35 |
|
H |
Hardened Steel |
Hardened Steel |
4500 |
HRC55 |
40-50 |